
DL-185 Dileucine (L-Leucyl-L-Leucine Monohydrate) – 2,000 mg
If we want to understand why dileucine helps build muscle, we should ask what role this peptide plays in human physiology under normal conditions. Does it occur naturally in the human body?
Yes, it does. Although you might expect digestion to break down amino acids like leucine into simpler parts, research has shown that the main products of gastrointestinal BCAA metabolism are actually peptides that contain the BCAAs as building blocks. One of these natural peptide metabolites is – you guessed it – dileucine.[6]
This means that the body goes out of its way to package leucine into dileucine. Given that the body is generally “lazy”, it would only do this if there was a really good reason for it.
It turns out that these peptide metabolites are responsible for much of the BCAA’s anabolic effect.[6] The more of these peptides you have circulating in your blood, the more efficiently your body can build muscle.
So, if we want to compare the effectiveness of oral leucine vs. oral dileucine supplementation, one way to do it might be seeing which supplement increases serum dileucine levels most effectively.
And that’s exactly what a team of researchers set out to do in 2021.
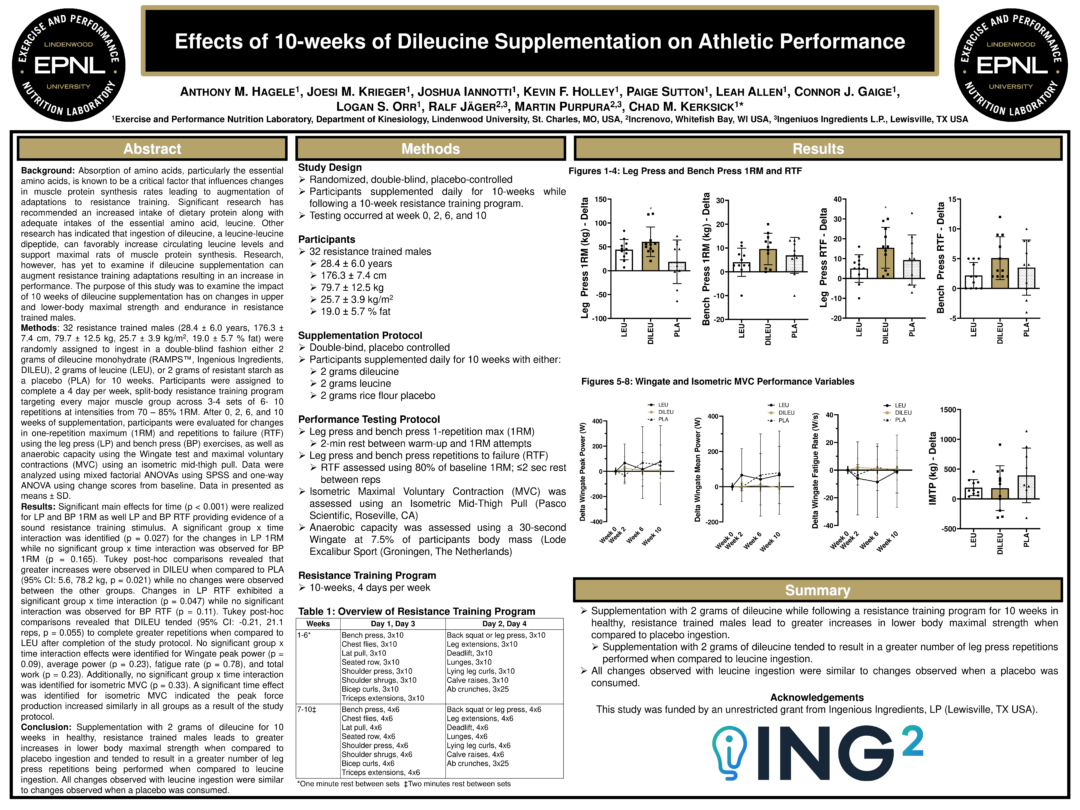
Effects of 10-weeks of Dileucine supplementation on athletic performance
Leucine vs. Dileucine in research
In an experiment detailed in the Journal of Applied Physiology, researchers recruited 10 healthy young men with an average age of 23 to compare 2 grams of leucine against 2 grams of dileucine. After providing it for breakfast, they then measured several dimensions of the subjects’ postprandial response to the treatment conditions.[8]
In the days leading up to the trial, the subjects were instructed to refrain from alcohol consumption, which can decrease muscle protein synthesis, and from exercise, which can increase it. They even gave the two groups an identical dinner the night before the test, which occurred at 7 a.m. the following morning.[8] The researchers took pains to isolate the treatment condition as the sole variable in the subjects’ muscle turnover activity after ingestion.
Although the sample size was relatively small, the study design was robust – it was a randomized, double-blind, crossover study, meaning the subjects completed the study twice — once for each treatment condition. That is, in the first round group A got the dileucine and group B got the leucine, then when the study protocol was repeated, group B got the dileucine and group A the leucine.
Crossover studies are a good way to make up for small sample sizes, and thanks to this study design, the effective sample size in each group was 20 instead of 10.[8]
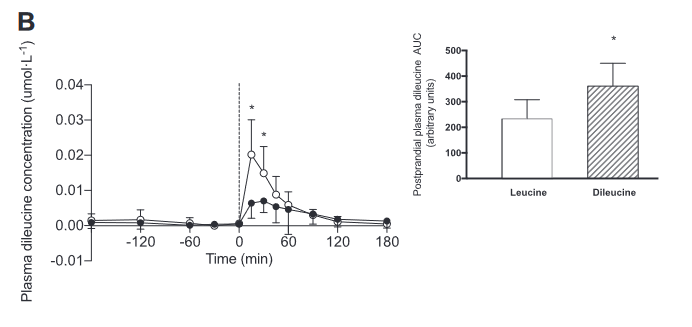
Compared to oral leucine supplementation, oral dileucine supplementation increased serum dileucine concentration more effectively.[8]
The researchers found that the dileucine supplement raised dileucine blood levels more effectively than the leucine supplement.
While this result is great, it’s also expected. So your next question is likely: So what? Did more dileucine in the blood translate to faster muscle protein synthesis?
Fortunately, the researchers looked at that too:
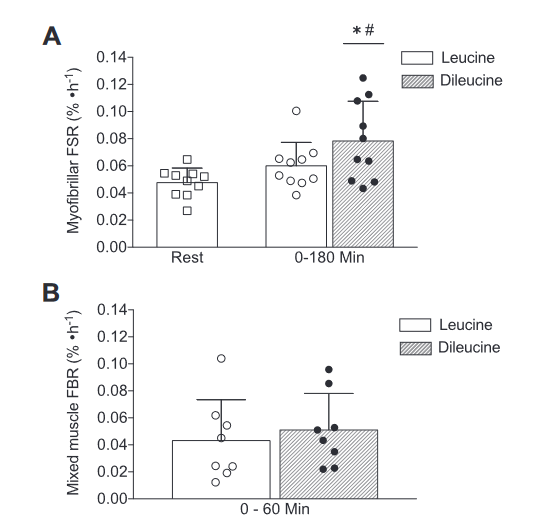
Oral dileucine supplementation increased fractional synthesis rate (FSR). Post-hoc analysis revealed no statistical difference in fractional breakdown rate (FBR).[8]
At first glance, it might appear that our inset graph is showing an increase in fractional synthesis rate (FSR), which is basically muscle building and fractional breakdown rate (FBR), which is muscle breakdown.
However, statistical analysis reveals that only the difference in FSR was significant. Here’s a quote from the abstract:
“Cumulative (0–180 min) MPS increased in DILEU (0.075 ± 0.032%·h1), but not in LEU (0.047 ± 0.029%·h1; P = 0.023). MPB did not differ between LEU (0.043 ± 0.030%·h1) and DILEU conditions (0.051 ± 0.027%·h1; P = 0.659).”[8]
If that’s confusing, the bottom line is that dileucine had a greater net anabolic effect compared to leucine. In fact, parsing the numbers in that quoted excerpt, we see that the dileucine increased MPS by roughly 160% compared to baseline, and roughly 60% more than leucine![8]
The authors conclude the paper by recommending that dileucine be explored as a food additive for populations at high risk of sarcopenia (age-related muscle wasting).[8] But we know where those types of results often lead… so researchers continued to press on:
ISSN 2023: 2g Dileucine vs. Leucine in 32 Resistance-Trained Males
In another study, which was presented in 2023 at the 20th International Society of Sports Nutrition (ISSN) Conference, 32 resistance-trained males with an average age of 28 were randomly assigned to receive either 2 grams of dileucine, 2 grams of leucine, or 2 grams of resistant starch (which served as a placebo control) for 10 weeks.[9,10]
While taking their assigned treatment condition, the subjects carried out a 4-day-per-week bodybuilding split workout routine, designed to hit every major muscle group with 3-4 sets of 6-10 repetitions. This was covered in two separate presentations at ISSN 2023.[9,10]

The researchers tracked changes in one-repetition maximum (1RM) and repetitions to failure (RTF) using the leg press (LP) and bench press (BP) exercises, as well as anaerobic capacity using the Wingate test and maximal voluntary contractions (MVC) using an isometric mid-thigh pull.[9]
In terms of strength, the study found no significant difference between leucine and the placebo. However, dileucine improved the subjects’ lower body maximal strength and maximum number of leg press repetitions before failure.[9]
The researchers also assessed the subjects’ body composition at weeks 0, 2, 6, and 10 using DEXA scan, finding no significant differences there.[10] However, the strength gains found are quite promising!
Generally, ISSN poster presentations get published in peer-reviewed journals later on in time, so make sure you stay tuned to PricePlow to learn when more details can be shared.
University of Toronto: 2g Dileucine + 1g Leucine vs. 6g 2:1:1 BCAA vs. Collagen
Finally, we have a third study carried out by the Faculty of Kinesiology and Physical Education at Canada’s University of Toronto.[11]

While this study is interesting, and we can’t see anything wrong with its design, we are nonetheless obliged to point out that it hasn’t yet been published in an academic journal, meaning it hasn’t gone through the peer review process. You, the reader, will have to decide how much you care about this.
With that disclaimer out of the way, let’s talk about the study.
This was another randomized, double-blind, crossover study. Twelve healthy adults – 8 men and 4 women – with an average age of 24 carried out roughly an hour of whole-body resistance training, after which they ingested one of three drinks containing:[11]
- 2 grams of dileucine and 1 gram of leucine (DIEAA)
- 3 grams of leucine, 1.5 grams of isoleucine, and 1.5 grams of valine (BCAA)
- Isonitrogenous serving of collagen protein (COL)
Isotope Tracked to Measure Leucine Retention
A clever aspect of this study design was the use of a leucine isotope to track how the subjects metabolized leucine under each treatment condition. Each drink contained 100 milligrams of the isotope, and the researchers used a breath test to measure how much of this isotope each group was exhaling for up to six hours after ingestion.[11]
Using the exhalation rate of this isotope as a measure of leucine oxidation, the researchers subtracted that oxidation from the subjects’ leucine intake. The resulting difference was taken as their leucine retention – i.e., the amount of leucine they were actually using to build new muscle.[11]
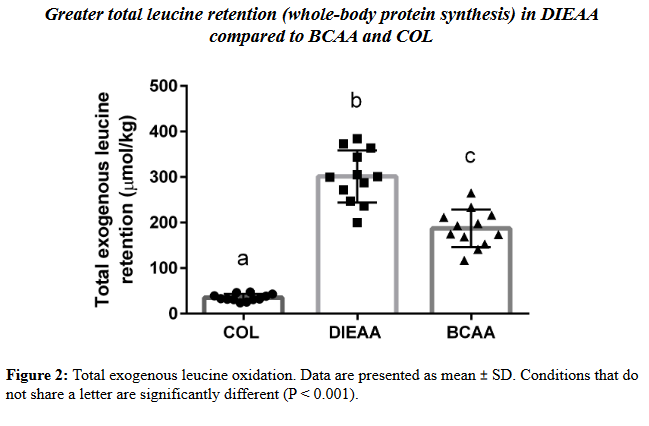
The DIEAA group showed vastly greater leucine retention than either BCAA or COL.[11]
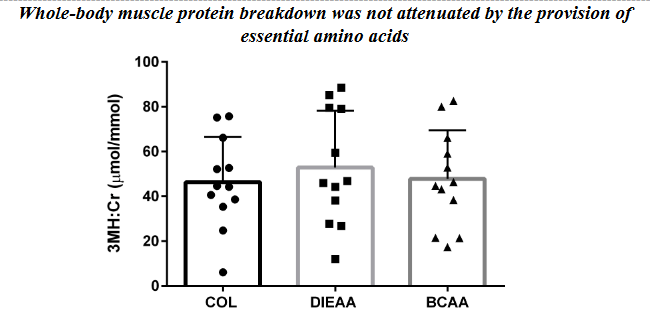
The provision of DIEAA, but not BCAA, significantly reduced muscle breakdown in response to whole-body resistance training.[11]
Not only did the DIEAA group show much greater leucine retention, they also suffered a lot less muscle protein breakdown in response to the exercise bout.[11] Both factors should contribute significantly to net muscle increase.
While much of this is not yet published in peer-reviewed journals, we’re confident that it’s certainly coming, and will keep PricePlow Nation apprised as it happens.
It should also be noted that MuscleTech Peptide does not contain the extra gram of leucine that was used in this study, but we’re pretty sure anyone reading this knows how to find some leucine if wanting to replicate this study!





